動きはぎこちないですが、一通りPI CARキットを操作できるようにりましたので、次は自律制御に挑戦してみようと思います。前回の試験ででは一升瓶を回ってスタート地点に戻ってくるテストを行いましたが、できればあれを自動でやりたいと思い立ちました。
現在のところ、自身には何の知識もありませんので、何から手を付けてよいのかわかりません。
ですが、周回対象のオブジェクトを検知する必要がありそうだなと思い、今回は、YOLOv5を試してみることにしました。まずは、Raspberry PI3で使い物になるかどうかを試してみてから、使い方を考えてみることにしました。
■ YOLO v5の準備
Raspberry PIにYOLO v5を下記のように導入します。(githubの記述に従っただけです)
ここではworkspaceの下にyolov5を導入します。
$ cd workspace $ git clone https://github.com/Ultralytics/yolov5.git $ cd yolov5 $ pip3 install -r requirements.txt $ pip3 uninstall torch torchvision $ pip3 install torch==1.11.0 torchvision==0.12.0
■ 動作確認
動作確認は下記のようなpythonコードをworkspace直下に用意して、YOLO v5の動作確認とともに動作スピードの確認を行いました。
学習データは、テストですのでyolov5直下にある‘yolo5s.pt’を使用しました。
import glob
import torch
import cv2
import shutil
import math
if __name__ == '__main__':
# this configures detection paramters.
model = torch.hub.load('./yolov5', 'custom',
path='./yolov5s.pt', source='local');
model.conf = 0.5
capture = cv2.VideoCapture(0)
while (True):
ret, frame = capture.read()
if ret:
# this detects objects.
results = model(frame)
# this converts color order.
results.save(save_dir="tmp")
img = cv2.cvtColor(cv2.imread("tmp/image0.jpg"), cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB)
shutil.rmtree("tmp")
# this displayes information of each objects.
results.print()
height, width = img.shape[:2]
for idx, row in enumerate(results.pandas().xyxyn[0].itertuples()):
xmin = math.floor(width * row.xmin)
xmax = math.floor(width * row.xmax)
ymin = math.floor(height * row.ymin)
ymax = math.floor(height * row.ymax)
print(row.name, ':(', xmin, ',', ymin, ')-(', xmax, ',', ymax,
'):', row.confidence)
cv2.imshow('camera', img)
if cv2.waitKey(1) & 0xFF == ord('q'):
break
capture.release()
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
画像出力とともに検知しているオブジェクトなどを確認しましたが、それなりに動作しているように見えます。
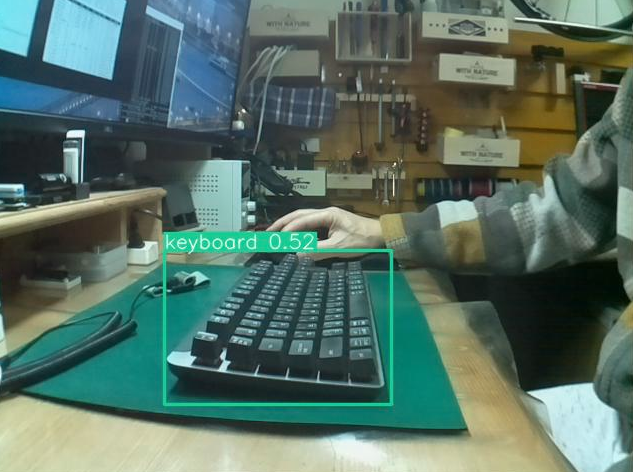

■ 性能評価
画像解像度は640×480で、大体1フレームあたりの処理時間が4~6秒程度かかっています。
さらには、CPU使用率の問題があり、下記のようにCPU使用率=400%となっています。Raspberry PI3のコアが完全燃焼してます。
YOLO v5のデモデータということもあり、結構なクラスが学習されているからなのかもしれませんが、この値を見る限りでは、常に検知状態で使用するのはまず無理だと分かりました。
PID USER PR NI VIRT RES SHR S %CPU %MEM TIME+ COMMAND
10021 --- 20 0 1373180 497080 129648 R 400.0 56.7 14:52.31 python3
10038 --- 20 0 10524 3260 2668 R 29.2 0.4 0:00.20 top
803 root 20 0 7588 1936 1760 S 4.2 0.2 0:02.67 apache2
10007 root 20 0 0 0 0 I 4.2 0.0 0:01.01 kworker+
10034 root 20 0 0 0 0 I 4.2 0.0 0:00.16 kworker+
■YOLOv5のROS2ビルド環境への影響
YOLOv5を導入後、ROS2で下記のようにパッケージビルドを行うとワーニングが発生するようになりました。
/.local/lib/python3.10/site-packages/setuptools/command/develop.py:40: EasyInstallDeprecationWarning: easy_install command is deprecated.
!!
********************************************************************************
Please avoid running ``setup.py`` and ``easy_install``.
Instead, use pypa/build, pypa/installer or other
standards-based tools.
See https://github.com/pypa/setuptools/issues/917 for details.
********************************************************************************
!!
easy_install.initialize_options(self)
理由は、YOLOv5とROS2で使用するsetuptoolsのバージョンが以下のように異なるためのようです。
| ROS2 humbleの推奨バージョン | YOLOv5の推奨バージョン |
| 58.2.00 | 69.2.0 |
YOLOv5インストール後のsetuptoolsのバージョンを確認すると、以下のように更新されていました。
$ pip3 list | grep setup
colcon-python-setup-py 0.2.8
setuptools 69.2.0
考えられる対処法は、2つあると思います。
1つ目の方法は、下記のような方法でsetuptoolsをダウングレードする方法です。
setuptoolsをダウングレードしてもYOLOv5は動作するようですが、非推奨となってしまうので、あまりよろしくありませんので、今回は実施しませんでした。
$ pip3 install setuptools==58.2.00
2つ目は、特定のワーニングを消し去る方法です。
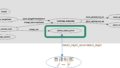
.bashrcに下記の記述を行いワーニングを無視するように設定します。
緑部分を”ignore:”に変更すると全ワーニングが表示されなくなります。
今回は、対象のワーニングだけを消したいので、下記のように設定しました。
PYTHONWARNINGS="ignore:easy_install command is deprecated."
export PYTHONWARNINGS
■ 次回
YOLO v5とROS2の共存ができそうなところまでは確認できました。
次回は、YOLOv5をROS2に組み込んでいこうとおもいます。
また、よろしければ見ていただけるとありがたいです。